 Abdominal Wall Defects
Abdominal Wall Defects
 Major Disorders: Omphalocele, Gastroschisis
Major Disorders: Omphalocele, Gastroschisis
@
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
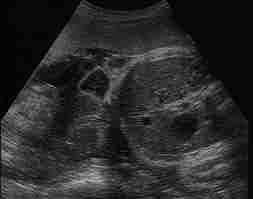
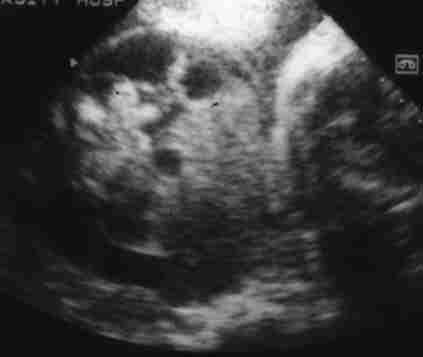
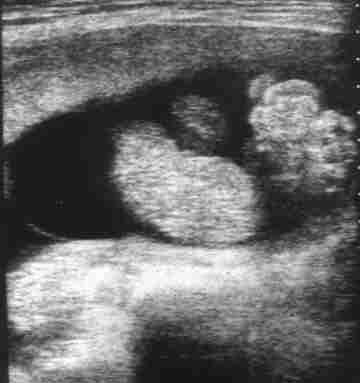
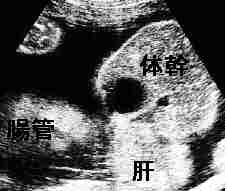
Gastroschisis: Evisceration excluding the liver without a covering membrane,
Insertion of the umbilical cord onto the abdominal wallI
Giant Omphalocele: Evisceration including the liver with an intact covering
membrane, Insertion of the umbilical cord into the covering membrane
Ruptured giant omphalocele: Evisceration including liver with ruptured covering
membrane, Insertion of the umbilical cord into the covering membrane
Ruptured giant omphalocele: Evisceration including liver without a covering
membrane, Insertion of the umbilical cord onto the abdominal wall or liver
 Prognostic factors in fetal omphalocele: Ruptured or absent covering
membrane with evisceration including the liver, Deformity of the spine,
Intrauterine growth returdation, Associated anomalies (severe cardiac anomalies,
severe chromosomal anomalies)
Prognostic factors in fetal omphalocele: Ruptured or absent covering
membrane with evisceration including the liver, Deformity of the spine,
Intrauterine growth returdation, Associated anomalies (severe cardiac anomalies,
severe chromosomal anomalies)
 Fetuses with giant omphalocele requires the protection of the preturm
labor, cesarian section and respiratory management immediately after birth.
Fetuses with giant omphalocele requires the protection of the preturm
labor, cesarian section and respiratory management immediately after birth.
 Giant omphalocele is sometimes complicated with pulmonary hypoplasia
which may have no indication for the treatment. Therefore, fetal diagnosis
should be made earlier than 20 gestational weeks.
Giant omphalocele is sometimes complicated with pulmonary hypoplasia
which may have no indication for the treatment. Therefore, fetal diagnosis
should be made earlier than 20 gestational weeks.
 The outcome of gastroschisis is generaly excellent. However, rare
cases develop fetal death and respiratory failure after birth.
The outcome of gastroschisis is generaly excellent. However, rare
cases develop fetal death and respiratory failure after birth.
Program for Prenatal Diagnosis
Pediatric SurgeryAOsaka University



