 Bronchopulmonary Anomalies
Bronchopulmonary Anomalies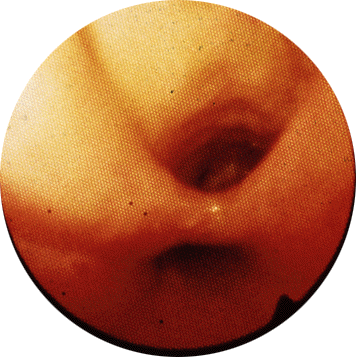
 Bronchopulmonary anomalies develop respiratory failure early after
birth. These consist of cystic lung disease and tracheobronchial
anomalies. Fetuses with these anomalies are usually complicated with
polyhydramnios, plural effusion and ascites which may
be a clue to a diagnosis.
Bronchopulmonary anomalies develop respiratory failure early after
birth. These consist of cystic lung disease and tracheobronchial
anomalies. Fetuses with these anomalies are usually complicated with
polyhydramnios, plural effusion and ascites which may
be a clue to a diagnosis.
 Cystic lung disease: Congenital
cystic adenomatoid malformatio of the lung (CCAM) and pulmonary
sequestration (including bronchogenic cyst and cases associated with
CCAM and bronchogenic cyst) are included.
Cystic lung disease: Congenital
cystic adenomatoid malformatio of the lung (CCAM) and pulmonary
sequestration (including bronchogenic cyst and cases associated with
CCAM and bronchogenic cyst) are included.
 Tracheobronchial anomalies:
Esophageal atresia (tracheo-esophageal fistula), laryngotracheal esophageal
cleft, laryngeal atresia, tracheal atresia (agenesis), bronchial atresia,
bronchopulmonary foregut malformation (BPFM), unilateral pulmonary hypoplasia
etc. These cases are sometimes associated with congenital tracheal stenosis.
Tracheobronchial anomalies:
Esophageal atresia (tracheo-esophageal fistula), laryngotracheal esophageal
cleft, laryngeal atresia, tracheal atresia (agenesis), bronchial atresia,
bronchopulmonary foregut malformation (BPFM), unilateral pulmonary hypoplasia
etc. These cases are sometimes associated with congenital tracheal stenosis.
 laryngotracheal esophageal cleft
laryngotracheal esophageal cleft
 Screening tests
Screening tests
 the
sagittal section of the upper thorax: checkup for a cyst in the upper mediastinum
(esophageal atresiaj
the
sagittal section of the upper thorax: checkup for a cyst in the upper mediastinum
(esophageal atresiaj
 the
transverse section of the thorax: measurement of lung/thorax
transverse area ratio (L/T)Acheckup for lung echogenesity and pleural
effusion
the
transverse section of the thorax: measurement of lung/thorax
transverse area ratio (L/T)Acheckup for lung echogenesity and pleural
effusion
 the
sagittal section of the thorax and abdomen: checkup for the echogenesity
of the lung/liver and ascites, measurement of chest/trunk
length ratio (C/T)
the
sagittal section of the thorax and abdomen: checkup for the echogenesity
of the lung/liver and ascites, measurement of chest/trunk
length ratio (C/T)
Program for Prenatal Diagnosis
Pediatric SurgeryAOsaka University
 laryngotracheal esophageal cleft
laryngotracheal esophageal cleft