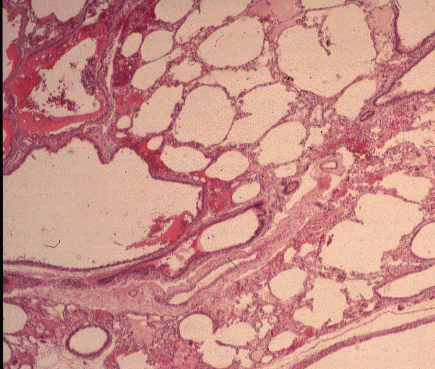
 Cystic Lung Disease
Cystic Lung Disease
 Classification of the cystic shadows:
Classification of the cystic shadows:
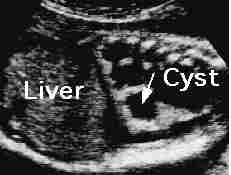
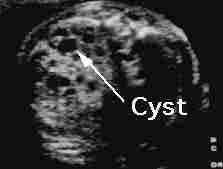
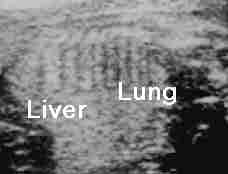
Type I: including at least a large cyst (>1 cm in diameter), Type II:
consists of small cysts (<1 cm in diameter), Type III: echogenic mass
 Differential diagnosis:
Differential diagnosis:
Since both diseases presents all types of cystic shadows, differential diagnosis
may be impossible from the cystic shadow. L/T ratio in pulmonary sequestration
usually increases after 32 weeks gestation.
In addition, differentiation from other diseases (diaphragmatic
hernia, tracheobronchial anomalies etc.) should
be required.
 Assessment of the severity:
Assessment of the severity:
measurements of lung/thorax transverse ratio (L/T)Afetal
hydrops
 Intrauterine treatment:
Intrauterine treatment:
Fetal hydrops in cases with type I lesion may be improved by aspiration
of cysts. Since the lesions in pulmonary sequestration and bronchogenic
cyst may shrink naturally, aspiration of cysts and fetal surgery should
be limitted in cases with fetal hydrops.
 Therapeutic strategy:
Therapeutic strategy:
In severe cases (L/T<0.26), cesarian section is performed on the 36/37
weeks gestation. Respiratory management with HFOV and NO inhalation is desirable
immediately after birth. Early operation is indicated if preductal PaO2>40
torr. In cases with L/T<0.20, ECMO should be prepared.
 Results in our department:
Results in our department:
9 survivors of 11 cases
Bronchopulmonary Anomalies
Program for Prenatal Diagnosis
Pediatric SurgeryAOsaka University
 Cystic Lung Disease
Cystic Lung Disease Cystic Lung Disease
Cystic Lung Disease

